TGM1 series diesel locomotives
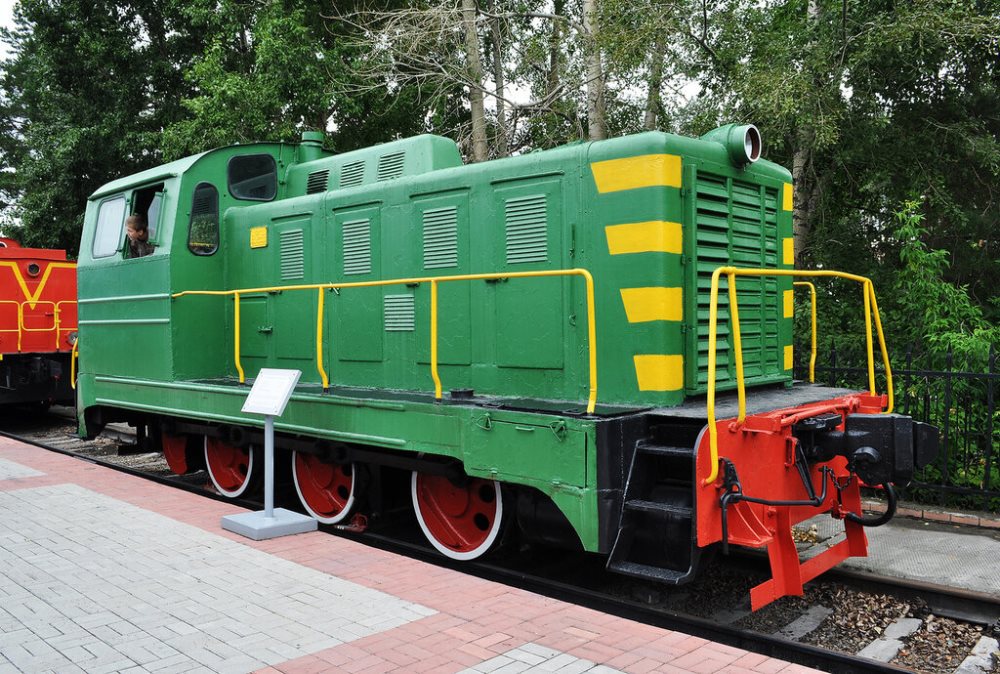 The TGM1 diesel locomotive is the first serial Soviet shunting diesel locomotive with hydraulic transmission, designed and built by the Murom Diesel-Locomotive Plant.
The TGM1 diesel locomotive is the first serial Soviet shunting diesel locomotive with hydraulic transmission, designed and built by the Murom Diesel-Locomotive Plant.
Story
In 1956, the Murom plant them. F.E. Dzerzhinsky built the first two three-axle shunting locomotives with hydrodynamic transmission. A diesel locomotive was designed at the same plant, inheriting the general layout of a captured German shunting diesel locomotive with hydromechanical transmission DG14-1. Since the new diesel locomotive was built as a replacement for 9P tank steam locomotives manufactured by the same factory, its power and thrust force became equivalent to the steam predecessor. Initially, the series was called TGM, then the designation was changed to TGM1 (diesel locomotive with hydraulic transmission, shunting).
In the process of producing a diesel locomotive, a number of changes were made to its design, concerning the scheme of electrical equipment, diesel engine management system, batteries, etc.
In the armored version was part of the armored trophy BTL-1
From 1956 to 1972, the plant produced 3369 diesel locomotives of the TGM1 series.
Most of the locomotives of this series worked at industrial enterprises, however, part of the locomotives was used for shunting work at railway stations.
Design
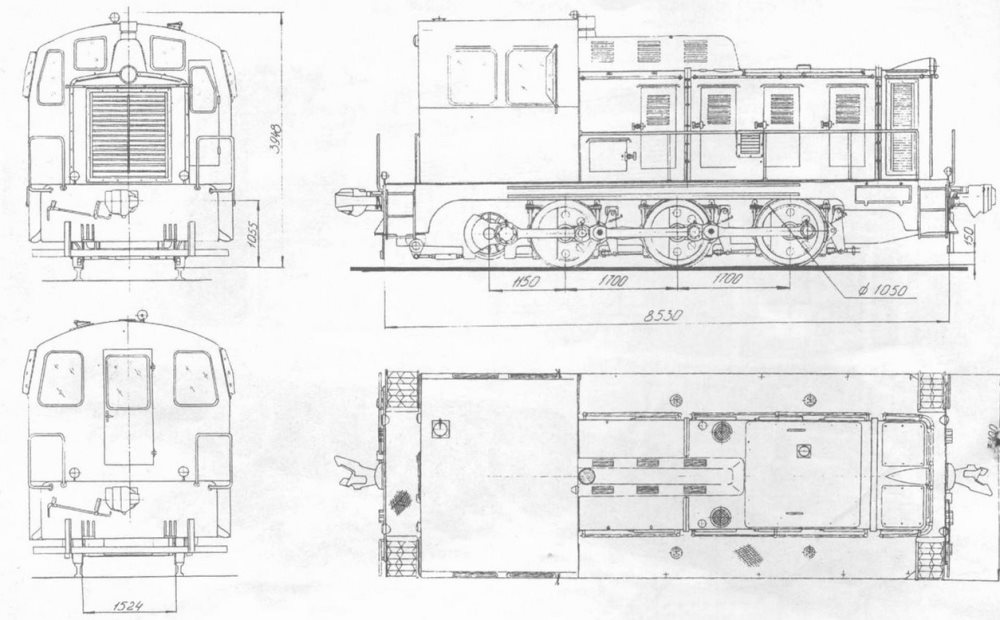
The body of the locomotive is of bonnet type, rigidly connected to the frame. Under the driver’s cab there is a baffle shaft connected to moving wheel pairs, which in turn are coupled, like a locomotive, with the help of steam guns. Diesel engine – twelve-cylinder four-stroke 1D12-400 with a capacity of 400 liters. with. production of the Barnaul plant.
At the first locomotive of the series, as well as at several subsequent ones, instead of the hydrotransfer of the Murom plant, the hydrotransfer of the German concern Voith GmbH was established, which was in fact exclusively building diesel locomotives for the whole world. The torque from the diesel to the wheelset was transmitted through the torque converter or one of the two hydraulic couplings (in various operating modes). The brake system was serviced by a compressed air compressor that was driven by a diesel engine. The driver controller had sixteen positions. Also in the management of the locomotive involved electromagnetic and electropneumatic valves. The water boiler was used for heating the driver’s cab and heating the oil, fuel and water during the cold season. However, the operation of the boiler was unreliable and in the future, instead of the boilers, the diesel was heated, and the driver’s cabin was heated with a heater.
Surviving specimens
To date, a number of TGM1 diesel locomotives have been preserved, both as exhibits in railway museums in the CIS and on the go, mostly owned by industrial enterprises. One of the oldest such diesel locomotives, TGM1-1503, built in 1963, operates in the SMP-738 Beltransstroy OJSC (Minsk).
Specifications
Maximum speed – 60 km / h
The maximum speed of the train mode is 50 km / h
Maximum speed of shunting mode – 30 km / h
Weight – 48 tons until 1965 release and 46 tons in the future
Copyright © New «Haivoron Diesel Locomotive Repair Plant» PJSC is with you from 2017. All rights reserved